The workplace is a melting pot of various generations, each bringing unique strengths and perspectives. However, bridging the gap between Gen Z, Millennials, and older generations like Baby Boomers and Gen X presents challenges. With different values, communication styles, and technological fluency, these age groups often find themselves at odds. The rapid evolution of technology and societal norms has widened this gap further, making collaboration challenging. Understanding these struggles is key to fostering a harmonious and productive work environment. Here are six reasons why younger and older generations often clash in the workplace.
1. Communication Styles

In today’s workplace, communication differences can create tension. Gen Z and Millennials often prefer quick, digital interactions like texting or instant messaging. Meanwhile, older generations may lean towards more formal communication, such as emails or in-person meetings.
These differing styles can lead to misunderstandings or perceived slights. For instance, a brief text message might seem too informal to a Baby Boomer. Such discrepancies require awareness and adaptation from both sides to minimize friction.
Adjusting communication methods can bridge these gaps, fostering better mutual understanding and collaboration. Finding common ground is essential for effective teamwork.
2. Work-Life Balance
Generational attitudes towards work-life balance differ significantly. Millennials and Gen Z often prioritize flexibility, valuing remote work and flexible hours. In contrast, older generations might see these preferences as a lack of commitment or discipline.
This disparity can lead to workplace tensions, as younger workers may feel constrained by rigid schedules. On the other hand, older colleagues might perceive flexibility as a lack of dedication.
Understanding and respecting these differences can lead to more harmonious workplace dynamics. Encouraging dialogue around expectations and responsibilities aids in fostering mutual respect.
3. Technological Fluency
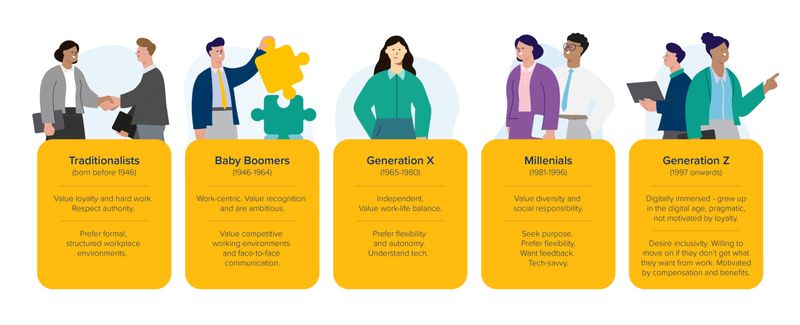
Tech fluency is another divisive factor. Gen Z and Millennials grew up in the digital age, making them adept with technology. Older generations might struggle to keep pace with rapid tech advancements.
This gap sometimes leads to frustration on both sides. Millennials may feel hindered by older colleagues’ slower tech adaptation, while older workers might feel alienated by constant tech changes.
Bridging this divide requires patience and collaboration. Younger employees can provide guidance, while older workers offer valuable experience. Together, they can create a balanced and innovative work environment.
4. Career Expectations

Career aspirations and expectations vary across generations. Younger workers often seek rapid career advancement and purpose-driven roles. Older generations might prioritize stability and longevity.
This difference can cause friction, with Gen Z and Millennials feeling stifled, while older workers see them as impatient or entitled. Aligning these perspectives is crucial for workplace harmony.
Open discussions about career paths and goals can help bridge this gap. Emphasizing mentorship and growth opportunities encourages understanding and mutual respect, leading to a more cohesive team.
5. Feedback Preferences
Feedback styles differ significantly. Gen Z and Millennials thrive on real-time feedback and dynamic learning environments. Older generations may favor structured, periodic evaluations.
The mismatch in expectations can lead to dissatisfaction. Younger workers may feel undervalued without regular feedback, while older workers might see constant feedback as micromanagement.
Balancing these preferences is key. Establishing a feedback culture that incorporates both real-time and structured methods ensures everyone feels valued. This approach nurtures growth and satisfaction across all age groups.
6. Cultural Values
Cultural values shape workplace dynamics. Younger generations often prioritize diversity, inclusivity, and social responsibility. Older generations might focus on traditional corporate values.
This divergence can lead to conflicts in workplace priorities and decision-making. Younger workers may see older colleagues as resistant to change, while older workers might view younger colleagues as overly idealistic.
Creating a culture that respects diverse values is essential. Encouraging open dialogue and understanding fosters a workplace where diverse perspectives can coexist harmoniously, leading to innovation and growth.

Well, hello there!
My name is Jennifer. Besides being an orthodontist, I am a mother to 3 playful boys. In this motherhood journey, I can say I will never know everything. That’s why I always strive to read a lot, and that’s why I started writing about all the smithereens I came across so that you can have everything in one place! Enjoy and stay positive; you’ve got this!

