In everyday conversation, even the most educated individuals can slip up by misusing certain words. This often leads to confusion, misunderstanding, or even embarrassment. Here, we explore 13 commonly misused words that frequently trip people up. By understanding the correct usage of these words, you can enhance your communication skills and avoid common pitfalls. Each word comes with a detailed description, an illustrative image prompt, and a relevant search query, making it easy to grasp their proper usage.
1. Ironic

Imagine a rainy day when you finally decide to leave the umbrella at home – is that ironic? The word ‘ironic’ is often misused to describe coincidences or unfortunate events. In reality, irony involves an outcome that is opposite to what was expected. This common misunderstanding can lead to perplexing conversations. Historically, irony has roots in ancient Greek theater, where characters spoke words with double meanings. By appreciating its true meaning, you can avoid the irony of using ‘ironic’ incorrectly. So, next time you encounter an unexpected twist, remember what irony truly entails.
2. Literally
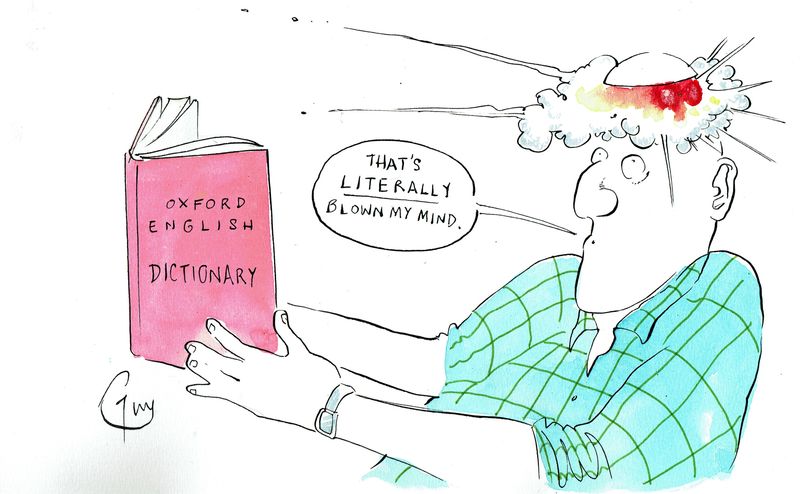

When someone says they’re ‘literally freezing’, are they really encased in ice? ‘Literally’ has become a staple in hyperbole, used to exaggerate situations that aren’t actually happening. This misuse dilutes its significance, as ‘literally’ should only describe actions or events that have truly occurred. In contrast, its overuse in exaggerated contexts has sparked debates among language purists. By preserving its original meaning, you contribute to the clarity and precision of language. Next time you reach for this word, consider whether it’s truly warranted – or if a figurative alternative might be more fitting.
3. Irregardless

‘Irregardless’ often appears in speech or writing, much to the dismay of grammar enthusiasts. Despite being used to mean ‘regardless,’ it’s technically nonstandard English. The correct word is ‘regardless,’ which conveys the same sentiment without the linguistic controversy. This word’s persistence in everyday language highlights the fluid nature of English. Remember, sticking with ‘regardless’ not only aligns with grammatical norms but also enhances your credibility in communication. Avoid the redundancy of ‘irregardless’ and embrace clearer expression by using recognized vocabulary.
4. Peruse

Does ‘peruse’ mean a casual glance or a thorough examination? Many use ‘peruse’ to suggest skimming through a document. However, its true meaning involves reading in great detail and with attention. This word’s misinterpretation can lead to confusion, especially in professional settings. Originating from Middle English, ‘peruse’ emphasizes careful consideration. By using it correctly, you enhance the precision of your communication. Next time you invite someone to ‘peruse’ a document, ensure you mean a detailed review rather than a mere overview. Embrace the depth this word offers in its proper context.
5. Unique

Is something ‘very unique’? The term ‘unique’ inherently means one of a kind, so using qualifiers like ‘very’ or ‘extremely’ is redundant. This misuse can diminish the word’s impact. In linguistics, ‘unique’ stands as an absolute term, needing no intensifiers. Historically, appreciation for the truly unique has been a cornerstone of artistic and cultural expression. By employing ‘unique’ in its intended form, you preserve its distinctiveness. When you encounter something truly unparalleled, resist the urge to add unnecessary emphasis and honor its singular nature with precise language.
6. Nauseous

Feeling queasy on a boat, are you ‘nauseous’ or ‘nauseated’? Many claim to be ‘nauseous’ when they experience sickness, but traditionally, ‘nauseous’ describes something causing nausea. The correct term for feeling ill is ‘nauseated.’ Linguistic precision matters, especially in contexts where clarity is vital. This distinction might seem minor, but it contributes to effective communication. Understanding these subtle differences enriches your vocabulary and aids in accurate expression. Next time you feel unwell, remember the distinction and choose the appropriate term to convey your discomfort accurately.
7. Enormity

The ‘enormity’ of a task often gets confused with its size. While many use ‘enormity’ to describe large scale, it traditionally denotes extreme wickedness or seriousness. This misinterpretation can lead to substantial misunderstandings, especially in written communication. Historically, ‘enormity’ carried connotations of moral outrage or grave importance. By recognizing its true meaning, you contribute to the richness and accuracy of language. When encountering a daunting challenge, consider whether ‘enormity’ accurately reflects its nature, or if another term might better capture its scope.
8. Disinterested

Are you ‘disinterested’ in this subject, or simply ‘uninterested’? The distinction is crucial, as ‘disinterested’ denotes impartiality, while ‘uninterested’ signals a lack of interest. This common confusion can alter perceptions, especially in academic or legal contexts. Understanding this difference enhances your communication skills. The historical significance of ‘disinterested’ lies in its association with fairness and unbiased judgment. By using these terms correctly, you contribute to precise language use. Next time you describe your level of engagement, ensure you’re conveying the intended message by choosing the right term.
9. Ambiguous
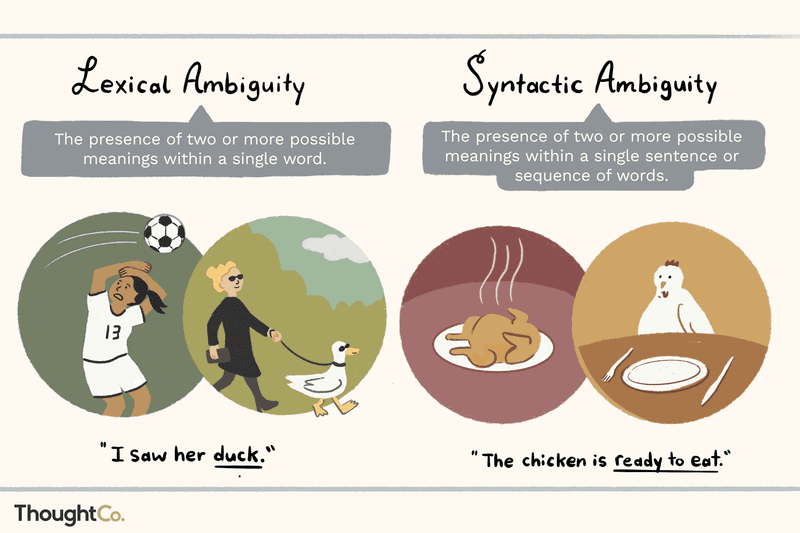
When a statement is ‘ambiguous,’ does it mean unclear or open to multiple interpretations? Often used to describe confusing messages, ‘ambiguous’ correctly implies potential for different meanings. This nuance is vital in legal and literary contexts. The roots of ‘ambiguous’ trace back to Latin, where it denoted double meanings. By understanding its true nature, you ensure clarity and precision in communication. Next time you encounter an ‘ambiguous’ phrase, consider the breadth of its interpretations rather than simply labeling it unclear. Embrace the complexity of language with informed expression.
10. Bemused

If you’re feeling ‘bemused,’ are you confused or entertained? While often mistaken for ‘amused,’ ‘bemused’ actually signifies bewilderment. This mix-up can lead to humorous misunderstandings. Historically, ‘bemused’ has been linked to a state of puzzlement, enriching its usage in literature. By distinguishing between these terms, you refine your expression and avoid potential misinterpretations. Next time you describe your reaction, ensure you’re conveying the right sentiment. Embrace the clarity that comes with understanding the true meaning of ‘bemused,’ and let your language reflect your intent accurately.
11. Affect vs. Effect

The ‘affect’ and ‘effect’ conundrum baffles many. ‘Affect’ is typically a verb, meaning to influence, while ‘effect’ is a noun, indicating the result of an influence. This distinction is crucial for clear communication. The roots of these words reflect their functions, with ‘affect’ linked to action and ‘effect’ to outcome. By mastering this difference, you enhance your linguistic precision. When discussing changes or impacts, ensure you’re using the correct term to convey your message effectively. Embrace the clarity that comes from knowing the right word for your intended meaning.
12. Compliment vs. Complement

Does your outfit ‘compliment’ your eyes, or does it ‘complement’ them? This common mix-up involves praise versus enhancement. ‘Compliment’ refers to expressing admiration, while ‘complement’ denotes completing or enhancing something. Understanding this distinction enriches your language. Historically, both words share Latin origins but have diverged in meaning. By using them correctly, you avoid misunderstandings and convey your message with precision. Next time you use these terms, ensure you’re expressing admiration or enhancement appropriately, preserving the integrity of your communication.
13. Anxious vs. Eager

Are you ‘anxious’ about the upcoming event, or ‘eager’ for it to begin? The distinction lies in emotion. ‘Anxious’ conveys worry, while ‘eager’ suggests anticipation. This difference is crucial for expressing feelings accurately. Historically, ‘anxious’ has roots in anxiety and apprehension, while ‘eager’ is linked to enthusiasm. By recognizing this nuance, you enhance your emotional communication. Next time you describe your feelings, choose the term that reflects your true sentiment. Understanding these subtle differences enriches your vocabulary and aids in precise expression.
Hi all, I am Sidney, an accountant, a hobbyist photographer, and a mother to two sweet girls who are my motivation. I love sharing the tips and tricks I gained all these years I’ve been a mother. I hope it will help you!

