Aging is a natural process that affects every living being. As we grow older, our bodies undergo numerous changes, some of which can be challenging to deal with. This article explores 15 distinct ways the human body deteriorates with age, shedding light on the physical and physiological transformations that occur over time. From the gradual decline in muscle mass to the subtle changes in skin texture, understanding these changes can help us better prepare for the inevitable journey of aging.
1. Muscle Mass Reduction

Muscle mass reduction is a common part of aging. With time, our muscles naturally lose strength and size, a process known as sarcopenia. This decline often begins in our 30s and accelerates as we age further.
Exercise plays a key role in slowing down this process. Resistance training and regular physical activity can help maintain muscle mass and strength, despite the years ticking by.
Interestingly, some studies suggest that diet, especially protein intake, plays a crucial role in preserving muscle tissue, providing a hopeful outlook for managing this aspect of aging.
2. Bone Density Loss
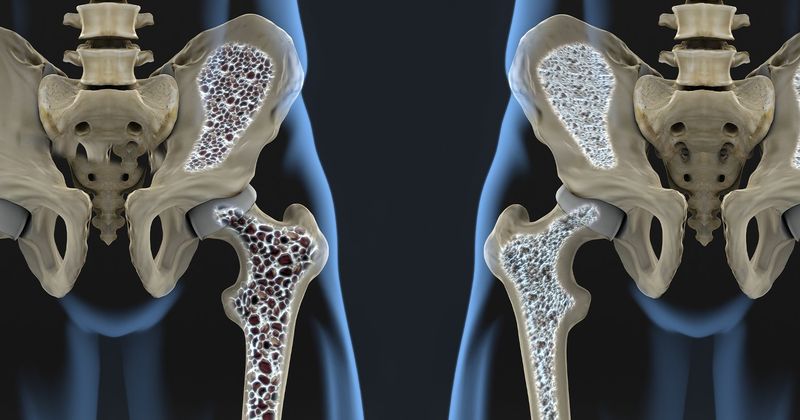
As we age, our bones undergo significant changes, often becoming more fragile. Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by decreased bone density, becomes more prevalent, particularly in post-menopausal women.
The body’s ability to regenerate bone diminishes with age, leading to a gradual weakening of the skeletal structure. This makes falls and fractures more likely and can severely impact mobility and independence.
Calcium and vitamin D play vital roles in bone health, and maintaining an active lifestyle can help mitigate bone density loss, offering a proactive approach to this aging challenge.
3. Skin Changes and Wrinkles

The skin, our body’s largest organ, reflects the passage of time. With age, it loses elasticity and moisture, leading to wrinkles and sagging. Collagen production slows, and the skin becomes thinner and more fragile.
Environmental factors like sun exposure and smoking can exacerbate these changes, highlighting the importance of skin care throughout life.
Despite these challenges, the beauty industry offers numerous products aimed at reducing the appearance of aging skin. Embracing these changes with grace and acceptance can foster a positive self-image as we age.
4. Vision Decline

Vision decline is a frequent companion of aging. Conditions such as presbyopia, cataracts, and age-related macular degeneration (AMD) become more common as we grow older.
Regular eye exams are crucial for early detection and management of these conditions. Glasses, contact lenses, or surgeries may become necessary to maintain clarity of vision.
Understanding the importance of eye health and taking proactive steps can help preserve vision, allowing one to enjoy life fully at any age, regardless of the natural changes that occur.
5. Hearing Loss
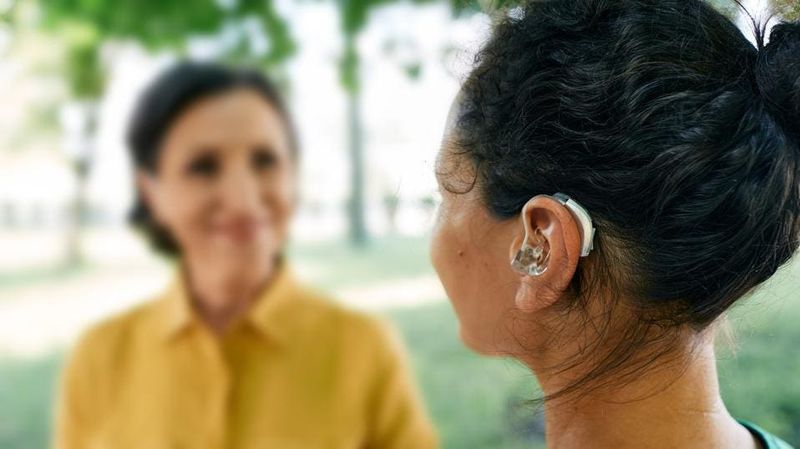

Hearing loss is a prevalent issue among the aging population. Presbycusis, the gradual loss of hearing in both ears, often occurs as we age. This can affect communication, leading to social isolation.
Hearing aids and assistive devices can significantly improve quality of life, allowing individuals to remain engaged with their communities. Interestingly, research suggests that staying socially active can help delay the progression of hearing loss.
Understanding and accepting the need for hearing support is vital in ensuring that connections with loved ones remain strong despite aging challenges.
6. Cognitive Decline

Cognitive decline is a natural part of aging. Memory lapses, difficulty concentrating, and slower information processing become more noticeable over time.
Engaging in mentally stimulating activities, such as puzzles and reading, can help keep the mind sharp. Maintaining social connections further supports cognitive health, as does a balanced diet rich in antioxidants.
While some cognitive decline is expected, understanding these changes can lead to more effective management strategies, allowing individuals to maintain mental acuity as they age.
7. Metabolism Slowdown

Metabolism naturally slows down as we age, leading to potential weight gain and decreased energy levels. This can affect overall health and wellbeing, making it important to adapt dietary habits accordingly.
Incorporating nutrient-rich foods and maintaining regular physical activity can help manage weight and energy levels.
Understanding metabolism’s role in aging empowers individuals to make informed lifestyle choices, ensuring that they continue to thrive despite the natural slowing of bodily processes.
8. Immune System Weakening
With age, the immune system becomes less robust, increasing vulnerability to infections and illnesses. This process, known as immunosenescence, means that older adults often experience more severe symptoms and prolonged recovery times.
Vaccinations, like the flu shot, become crucial in protecting against preventable diseases. Nutrition and exercise also play significant roles in supporting immune function.
While the weakening of the immune system is an inevitable part of aging, proactive healthcare measures can mitigate risks and maintain overall health.
9. Digestive System Changes
Aging affects the digestive system in various ways. Reduced production of digestive enzymes can lead to discomfort and nutrient absorption issues.
Increased risk of gastrointestinal conditions, such as constipation and acid reflux, is common among older adults. A diet rich in fiber and adequate hydration can alleviate these symptoms.
Recognizing and adapting to these digestive changes can improve quality of life, allowing individuals to enjoy meals without discomfort or worry.
10. Sleep Pattern Alterations
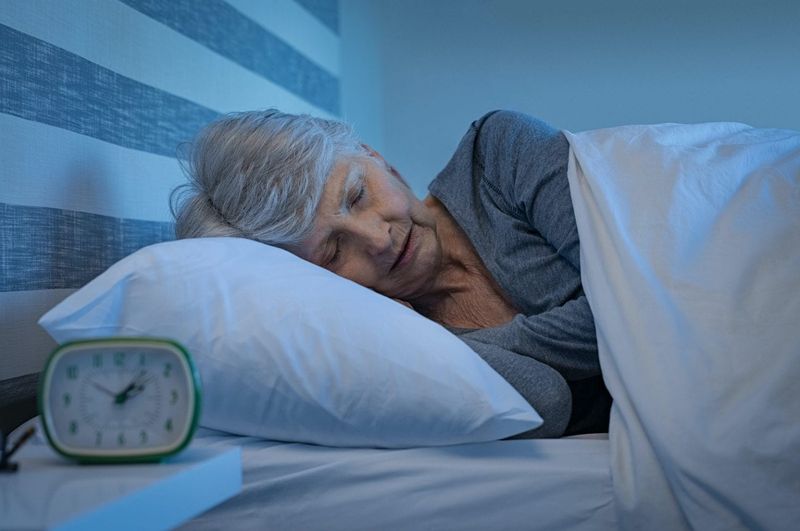

Sleep patterns often change with age. Older adults may experience difficulties falling asleep and staying asleep, leading to fatigue.
The importance of sleep hygiene cannot be overstated. Creating a comfortable and calming sleep environment, along with establishing a regular sleep routine, can enhance sleep quality.
While sleep disturbances are common, understanding the underlying causes and implementing strategies to improve sleep can greatly enhance overall wellbeing.
11. Cardiovascular Changes

Cardiovascular changes become apparent as we age. The heart and blood vessels undergo structural changes, leading to increased risk of hypertension and heart disease.
Regular physical activity and a balanced diet can support heart health, while regular check-ups allow for early detection of potential issues.
Understanding these changes empowers individuals to take proactive steps in maintaining cardiovascular health, ensuring a more active and fulfilling life well into their senior years.
12. Hormonal Fluctuations
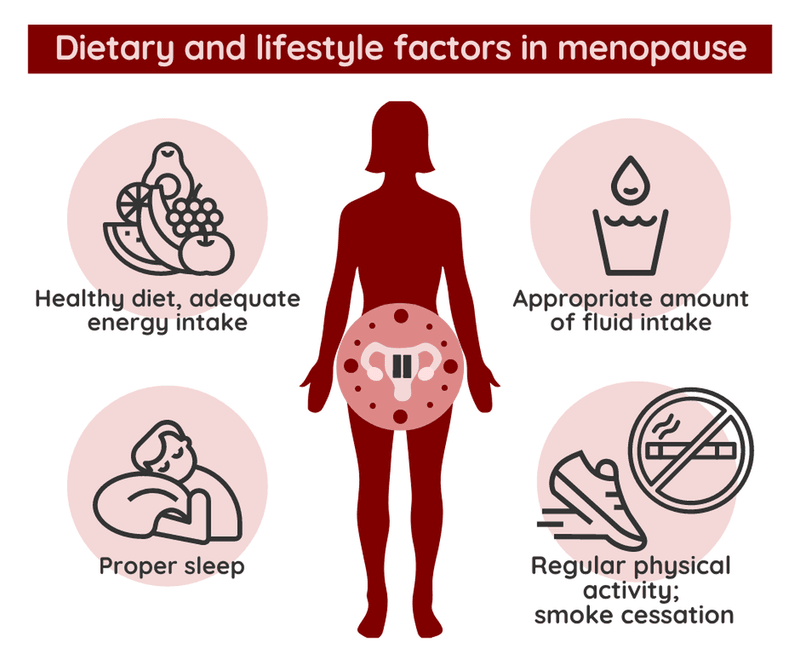
Hormonal fluctuations are a significant aspect of aging, particularly for women. Menopause brings about a decline in estrogen, leading to symptoms such as hot flashes and mood swings.
Hormone replacement therapy is an option for some, though lifestyle modifications can also offer relief. Managing stress and maintaining a healthy lifestyle plays a crucial role in navigating these changes.
Understanding hormonal shifts allows for more informed choices, helping individuals adapt to and manage these natural changes with grace.
13. Joint and Mobility Issues

Joint pain and mobility challenges often accompany aging. Conditions like arthritis can make movement difficult, affecting daily activities.
Physical therapy and low-impact exercise can enhance mobility and reduce pain. Maintaining an active lifestyle supports joint health, allowing for greater freedom and independence.
Recognizing and addressing joint issues early can prevent further deterioration and improve quality of life as individuals age gracefully.
14. Hair Thinning and Graying
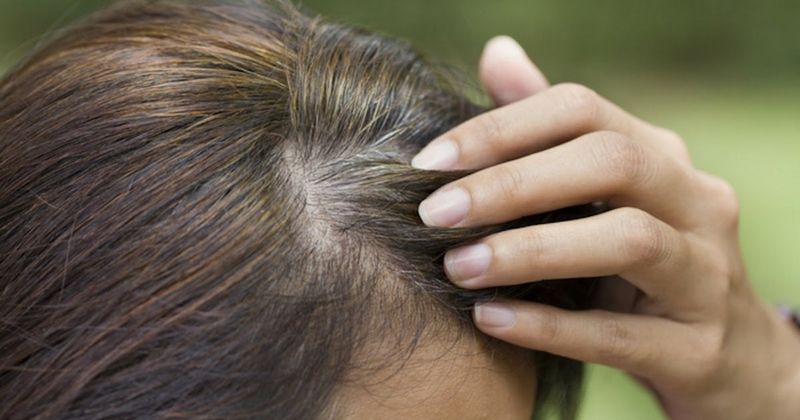

Hair thinning and graying are common signs of aging. Genetics plays a significant role in these changes, with hair losing its pigment and often becoming thinner.
Embracing these changes can foster confidence and self-acceptance. Many find joy in styling their gray hair in new ways, celebrating this natural transition.
Understanding that hair changes are a normal part of aging allows individuals to embrace their appearance, enhancing self-esteem and personal expression.
15. Taste and Smell Diminishment
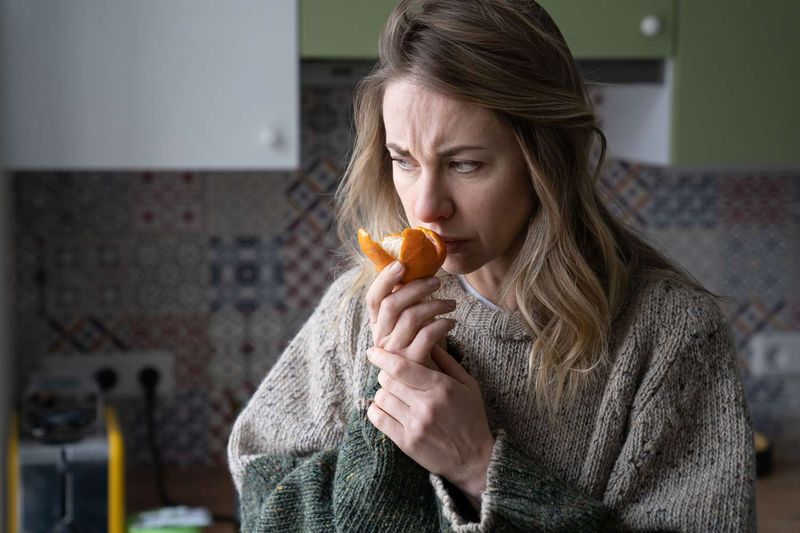

As we age, our senses of taste and smell can diminish, affecting appetite and enjoyment of food. This change is often gradual, but it can significantly impact nutrition and quality of life.
Enhancing flavors with spices and herbs can make meals more enjoyable. Ensuring adequate nutrition is vital, and regular dental care plays a role in maintaining taste and smell.
Understanding these sensory changes allows for adaptations that enhance meal satisfaction, ensuring that dining remains a pleasurable experience.

