Generation X parents, known for their resilience and independence, inadvertently nurtured an environment that contributed to heightened anxiety in their children. While their intentions were undoubtedly rooted in love and care, certain parenting strategies and choices have been linked to the rise of an anxious generation. Here’s a detailed exploration of these methods and their impacts.
1. Helicopter Parenting
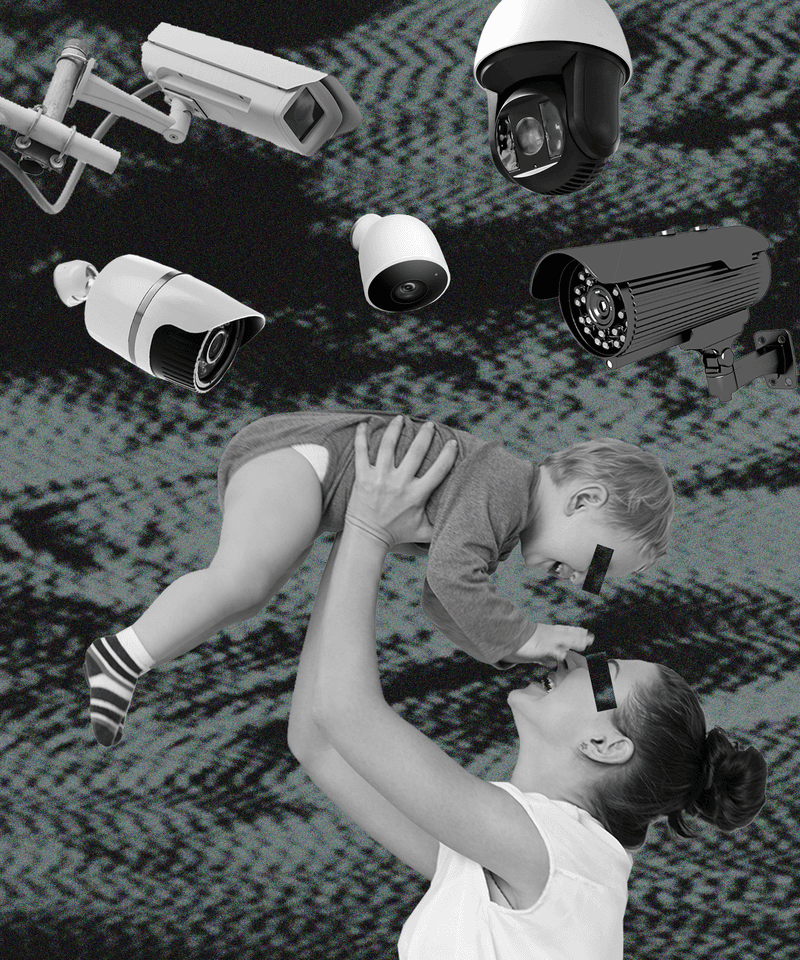
Hovering like a helicopter, these parents were always nearby, ever-watchful and ready to swoop in at the first sign of trouble. While their intentions were protective, this constant surveillance stifled the development of independence and self-confidence.
Children often felt scrutinized, leading to self-doubt. The lack of freedom fostered a sense of inadequacy, as kids weren’t given the space to fail and learn from mistakes.
This over-involvement paradoxically led to increased anxiety, as children grew up without the necessary coping mechanisms to handle challenges independently.
2. Academic Pressure

“Grades are everything,” was a mantra for many Gen X parents. The relentless focus on academic achievement meant children were often overwhelmed by expectations.
This pressure cooker environment left little room for exploration outside of academics, stifling creativity and personal growth. The fear of failure loomed large, adding to stress and anxiety.
As a result, children internalized the belief that their worth was tied to their academic success, creating a foundation for lifelong anxiety.
3. Over-Scheduling

From soccer practice to violin lessons, Gen X parents filled every hour of their child’s day. While the idea was to give them opportunities, it often resulted in burnout.
Children rarely had time to relax or pursue leisurely interests. This constant hustle left kids feeling exhausted and stressed, lacking time to process experiences.
The inability to unwind and reflect hampered emotional resilience, fueling anxiety as children struggled to cope with life’s demands.
4. Stranger Danger

“Don’t talk to strangers” became an anthem amid rising crime fears. Gen X parents, concerned for safety, passed their anxieties onto their kids.
This pervasive fear of the outside world fostered mistrust and social apprehension. Children learned to view the world as dangerous, inhibiting social development.
While safety is crucial, this hyper-vigilance contributed to generalized anxiety, as children lacked experience in navigating new social scenarios.
5. Boomer Parenting Influence

Shaped by their own boomer parents, Gen X absorbed traditional parenting styles that emphasized control and discipline.
This adherence to past methods, while seeking to improve upon them, often clashed with contemporary understanding of child psychology. The strict, authoritative approach created an environment ripe for anxiety.
As children sought to please their demanding elders, the pressure to conform and excel led to heightened stress and anxiety.
6. Tech-Driven Isolation

Technology’s boon was a bane for personal interactions. Gen X parents introduced kids to the digital world, often as a tool for learning and entertainment.
Yet, this reliance on screens fostered isolation, replacing face-to-face contact. The virtual world became a refuge, but also a source of social anxiety.
Navigating online interactions, children missed out on building real-world social skills, leading to increased feelings of loneliness and anxiety.
7. The Competitive Edge

In pursuit of excellence, Gen X parents encouraged relentless competition. From sports to academics, the drive to be the best was ever-present.
This constant competition instilled a fear of inadequacy. Success was celebrated, while failure became unacceptable, breeding anxiety.
The pressure to outperform peers overshadowed personal achievements, leading to chronic stress and a perpetual state of anxiety in children.
8. Safety Obsession

Ensuring safety became an obsession for many Gen X parents. Bubble-wrapped childhoods meant kids rarely faced risks, inhibiting the development of resilience.
This overprotective approach limited experiences necessary for learning and growth. Without risk, children struggled to develop confidence and adaptability.
The fear of harm created a narrative of vulnerability, contributing to increased anxiety as children encountered unfamiliar challenges.
9. Focus on Individualism

Encouraging individuality, Gen X parents often emphasized self-reliance and personal achievement over communal support.
While independence is valuable, the lack of emphasis on community and teamwork led to feelings of isolation. Children felt immense pressure to succeed on their own.
This focus on the self above community support systems intensified anxiety, as children lacked networks to lean on during tough times.
10. High Expectations

Gen X parents often upheld high expectations, dreaming of bright futures for their children.
While these aspirations were well-intentioned, they often translated into pressure and stress for kids striving to meet lofty goals. The fear of disappointing their parents added to their anxiety.
Struggling to balance their dreams with their parents’ expectations, children felt anxious about living up to ideals.
11. Emphasis on Success

Success became synonymous with happiness. Gen X parents, eager for their children to thrive, equated achievement with contentment.
This narrow view fostered anxiety, as children linked self-worth to accomplishments. The relentless pursuit of success overshadowed their ability to enjoy simple pleasures.
Focusing solely on achievements led to a perpetual cycle of stress, as children feared falling short of success.
12. Media Influence

The rise of media brought vivid, often alarming, stories into homes. Gen X parents, exposed to constant news cycles, couldn’t help but pass on their concerns.
Children, absorbing this media influence, grew wary of the world’s dangers. The depiction of reality as threatening fueled anxiety.
While awareness of current events is important, the incessant exposure to negative news heightened fears, contributing to a more anxious outlook on life.

