The United States has long been a land of movement, with individuals and families frequently packing their bags in search of better opportunities or a change in lifestyle. Recently, however, several states have seen a noticeable trend of residents leaving in significant numbers. Between July 2023 and July 2024, the data reveals a pattern where certain states are experiencing net domestic migration losses. Factors such as high living costs, taxes, and housing affordability are contributing to this exodus. These shifts not only affect the states losing residents but also have wider implications on demographics and local economies.
1. California
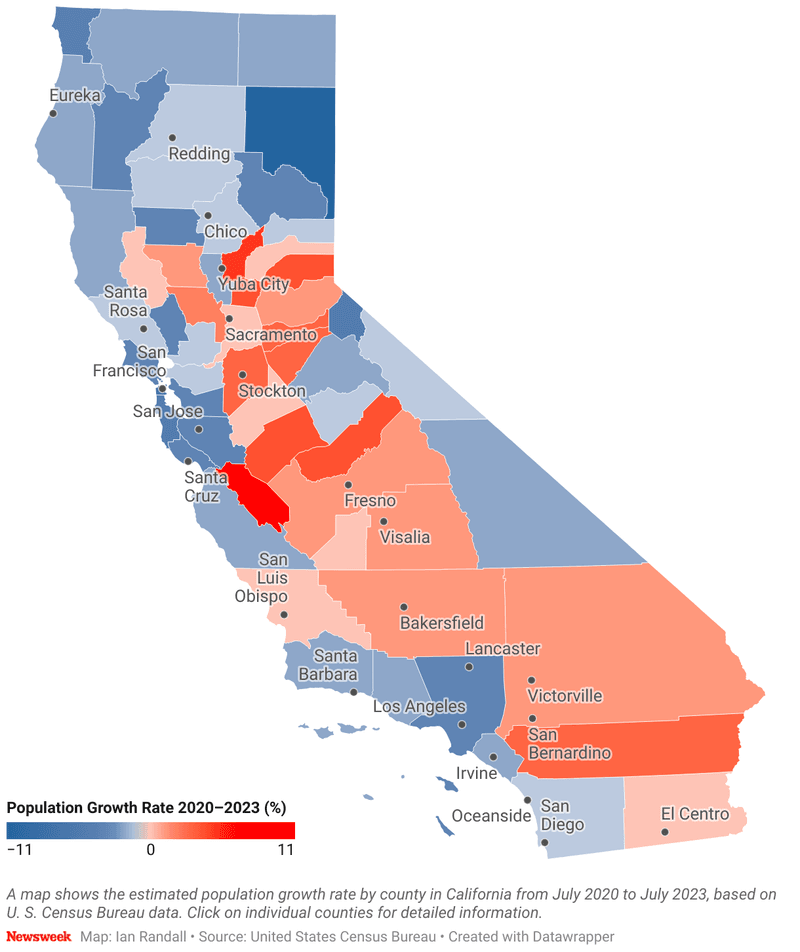
California, known for its golden beaches and bustling cities, is seeing a trend of residents leaving. With a staggering loss of 239,575 people, the state’s high cost of living and housing crisis are driving factors. The Golden State’s allure seems overshadowed by economic challenges, prompting many to seek affordability elsewhere.
The tech industry’s boom hasn’t been enough to stem the tide, as families and individuals opt for states with lower taxes and more reasonable housing prices. While California remains iconic, its towering expenses are making it less attractive for long-term residency.
2. New York

New York, with its iconic skyline and vibrant culture, lost 120,917 residents, sparking curiosity about the exodus. Often seen as the land of opportunity, the high cost of living and housing are major deterrents for many.
The Big Apple’s charm doesn’t outweigh these financial burdens, leading residents to seek greener pastures. As people leave the city that never sleeps, they carry with them dreams of affordability and space. This shift not only impacts New York’s population but also alters its cultural tapestry.
3. Illinois

Illinois, known for its heartland charm, has witnessed the departure of 56,235 residents, raising questions about its appeal. Economic concerns, such as taxes and fiscal instability, are often cited as reasons.
The Land of Lincoln’s struggles with budgetary woes have not gone unnoticed. As residents seek stability, neighboring states become attractive alternatives. Despite its rich history and cultural landmarks, Illinois faces challenges in retaining its populace, echoing broader Midwest migration patterns.
4. New Jersey

New Jersey, with its proximity to major cities and coastal allure, lost 35,554 residents. The Garden State’s high property taxes and living costs are significant factors.
The allure of nearby urban centers can’t offset these financial pressures, prompting many to relocate for economic relief. Known for its beautiful shorelines and bustling suburbs, New Jersey’s migration pattern reflects a search for fiscal sanity amidst escalating expenses.
5. Massachusetts

Massachusetts, renowned for its educational institutions and historical significance, saw 27,480 residents leave. Despite its intellectual allure, high living costs and housing prices are major deterrents.
As residents grapple with financial challenges, many are choosing states with more favorable economic conditions. The Bay State’s rich cultural tapestry remains, but its population dynamics are shifting as individuals seek a balance between tradition and affordability.
6. Michigan

Michigan, known for its automotive legacy, faced a decrease in population. Economic recovery and job prospects play a significant role in this migration.
As industrial shifts continue, many residents are drawn to states with burgeoning job markets and economic stability. The state’s natural beauty remains an asset, but economic factors are pivotal in migration decisions, reflecting broader industrial trends.
7. Louisiana
Louisiana, with its vibrant culture and rich history, saw residents leave for economic opportunities elsewhere. The state’s economy has been a driving factor in migration trends.
Natural disasters and economic challenges add to the complexities, prompting families to seek stability and security. While Louisiana’s cultural heart beats strong, its population dynamics are shifting as people prioritize economic resilience.
8. Ohio

Ohio, known for its diverse economy, has seen residents depart in search of better prospects. Economic opportunities and educational advancements often guide these decisions.
The Buckeye State’s industrial history remains, but emerging markets in other regions attract those seeking growth. As residents leave, Ohio’s demographic landscape changes, reflecting the push for innovation and opportunity beyond its borders.
9. Pennsylvania
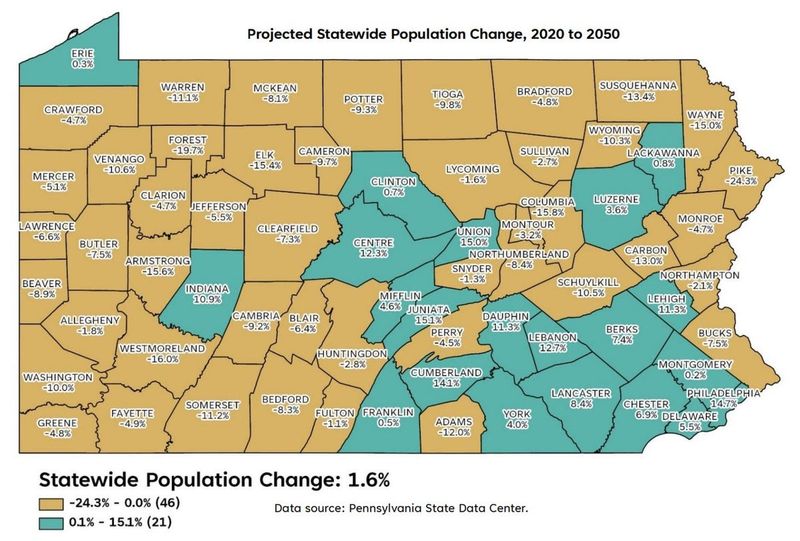
Pennsylvania, steeped in history, faced a population decline, with residents moving for economic reasons. The state’s rich traditions are juxtaposed with modern economic challenges.
The search for employment and affordable living drives migration, as individuals opt for regions with promising futures. Pennsylvania’s cultural depth remains, but its population shifts reveal broader economic trends.
10. Connecticut

Connecticut, known for its picturesque landscapes and quaint towns, saw residents leave due to economic factors. High living costs and taxes play a crucial role.
The Nutmeg State’s charm doesn’t fully offset its financial burdens, leading to a search for economic relief elsewhere. As families relocate, Connecticut’s demographic shifts reflect a broader quest for affordability and opportunity.

Well, hello there!
My name is Jennifer. Besides being an orthodontist, I am a mother to 3 playful boys. In this motherhood journey, I can say I will never know everything. That’s why I always strive to read a lot, and that’s why I started writing about all the smithereens I came across so that you can have everything in one place! Enjoy and stay positive; you’ve got this!

